Background: The management of patients with multiple myeloma (MM) has evolved significantly over the last two decades with increased utilization of autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (AHCT) and introduction of proteasome inhibitors (PIs) and immunomodulatory agents (IMIDs) and concomitant improvement in survival, particularly in younger patients. Both AHCT and the IMID lenalidomide have been associated with increased risk of second malignant neoplasms (SMN) in clinical trials, with the risk reaching 6.9% at 5 years in a recent meta-analysis. We intended to assess whether an increase in incidence of SMN was evident at the population level and the impact of the changing SMN risk on survival of MM patients.
Methods: We utilized the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results 13 (SEER 13) registries to analyze three cohorts of patients: those diagnosed during 1995-1999 (pre-thalidomide, limited use of AHCT, 15 years of follow up), 2000-2004 (post-thalidomide, pre lenalidomide and bortezomib, increased utilization of AHCT, 10 years of follow up) and 2005-2009 (post-lenalidomide and bortezomib, higher utilization of AHCT, 5 years of follow up). Follow up is current to the end of 2014. We included patients younger than 65 years at the time of diagnosis of MM as first malignant neoplasm to focus the analysis in patients more likely to receive AHCT and presumably prolonged lenalidomide exposure. For each cohort, we calculated the incidence of SMN considering death from any cause as a competing risk. Since comparison by era is subject to confounding by attained age, we analyzed and compared standardized incidence ratios (SIRs) for SMN and causes of death (COD) in intervals of 5 years: years 1-5 and years 6-10 from diagnosis.
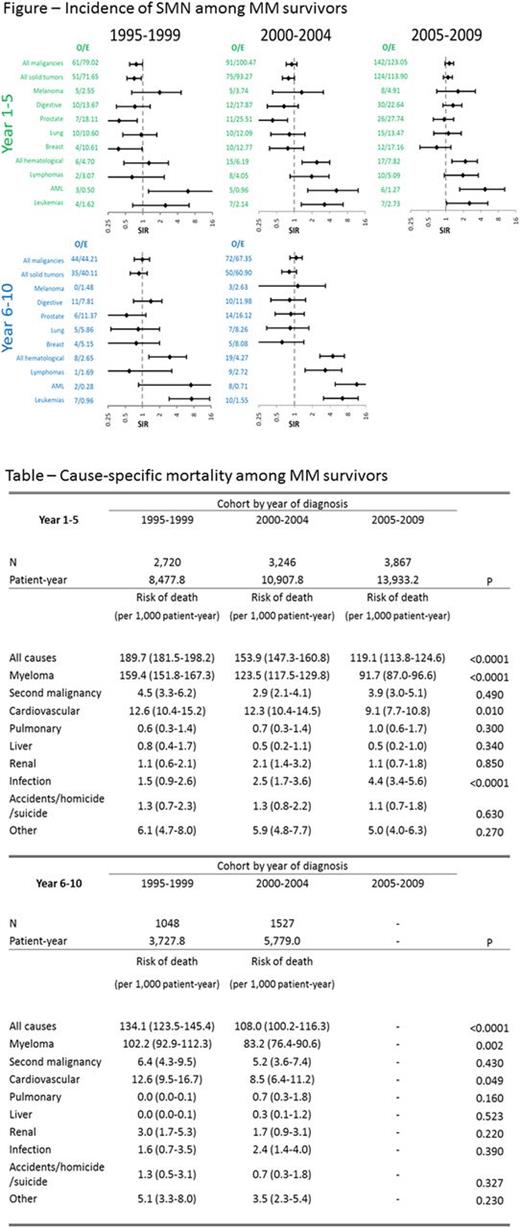
Results: There were 2,720 patients in the 1995-1999, 3,246 in the 2000-2004 and 3,867 in the 2005-2009 cohort. Median age of diagnosis was 56 years and 56.6% of the patients were males with no differences across cohorts. Non-Hispanic Whites were 55.9%, non-Hispanic Blacks 23.2%, Hispanics 12.6% and individuals of other race/ethnicities 8.2%. Median follow up of survivors was 198 months (range 1-239), 141 months (range 1-179) and 81 months (range 0-119) in the 1995-1999, 2000-2004 and 2005-2009 cohorts respectively. Cumulative incidences of SMN at 90 months were 4.7% (95% C.I. 4.0-5.6%), 6.0% (95% C.I. 5.2%-6.8%) and 6.3% (95% C.I. 5.5%-7.1%), respectively in the 3 consecutive cohorts, P=0.0008. The statistically significant, yet small increase in SMN is accompanied with decline in all-cause mortality in the same period from 69.9% for the 1995-1999 cohort to 60.4% for the 2000-2004 cohort to 52.8% for the 2005-2009 cohort, P<0.0001. During years 1-5 after MM diagnosis, the risk of another cancer of any type evolved from lower than expected in an age, gender and race-matched population for patients diagnosed in 1995-1999 (SIR=0.77, 95% C.I. 0.59-0.99) to similar to expected for patients diagnosed in 2005-2009 (SIR=1.15, 95% C.I. 0.97-1.36), driven particularly by increase in hematologic malignancies from SIR=1.28 (95% C.I. 0.47-2.78) to SIR=2.17 (95% C.I. 1.27-3.48),(Figure). For years 6-10, the overall risk of subsequent malignancy in MM survivors is similar to the matched population for both the 1995-1999 and the 2000-2004 cohorts (most recent cohort with 10-year follow up). However, the risk of subsequent hematologic malignancy is increased in both periods with the most substantial change being in the risk of lymphomas evolving from SIR=0.59 (95% C.I. 0.01-3.29) for the 1995-1999 cohort to SIR=3.31 (95% C.I. 1.51-6.27) for the 2000-2004 cohort. As expected, overall mortality in years 1-5 declined sharply across the three cohorts (Table), driven by decline in both MM-associated (from 159.4 to 91.7/1,000 patient-year) and cardiovascular mortality (from 12.6 to 9.1/1,000 patient-year). Importantly, there was no discernible increase in risk of death from SMN (from 4.5 to 3.9/1,000 patient-year).
Conclusions: This population study confirms that the evolution of MM therapy in the US in the last 20 years is associated with a small, statistically significant increase in the risk of SMN in patients <65 years. Such increase is driven mostly by the increased incidence of hematologic malignancies. The study also demonstrates that the mortality from SMN is modest, has not significantly increased over time and is obscured by the robust reduction in mortality from MM.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.